 |
Food Web Relationships - producer/consumer, predator/prey, or parasite/host "When we try to pick out anything by itself, |
1. Get the facts about - Food Chains and Webs
Food Chain and Food web | Meadow Food Chains, Kalman, Bobbie
Exploring Meadow Food Chains by Katie Kawa
Food Chains in a Meadow Habitat by Isaac Nadeau, Dwight Kuhn (Check your library)
2. Read the folk tale Sly Fox by Beulah Murrelle
![]() 3. Create a matrix (Need help? - Matrices @ Math Dude)
3. Create a matrix (Need help? - Matrices @ Math Dude) ![]()
Use the first row to label the Columns -
Animal Species - Predator - Prey - Producer - Consumer - Parasite - Host.
Down the first column, enter each animal species mentioned in the story.
(Skip the one in the simile.)
Or select 7 species found in meadows, fields and fencerows in your local/state.Enter 1 animal species in each row starting in row 2.
Use the matrix to sort out the relationships.
For each species :
Ask yourself - Is it a predator? If yes, place a
checkmark in the cell.
If no, leave the cell blank.Continue through each column and do all animal rows.
Examine the matrix - What have you found?
How many of the animals are predators?
What percentage of the animals are prey?
How many of the animals are producers?
What percentage are consumers?
Which relationship is represented the most in the story?
Which relationship is represented the least in the story?
What conclusion(s) can you come to using the information?
Extend your efforts:
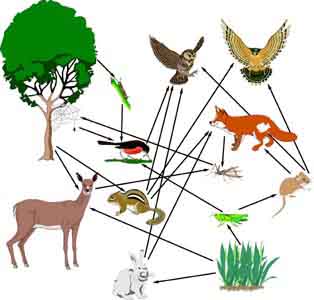
![]() Draw a food web of fields & meadow organisms. Show the flow of energy.
Draw a food web of fields & meadow organisms. Show the flow of energy.
(You do not have to draw pictures. Use public domain images. If you prefer, type the names and draw the arrows using the draw arrow tool.)
(doc. / pdf version of this activity for printing)
Fields, Meadows, and Fencerows: Habitat / Mammals / Birds / Insect - Butterflies & Moths / Trees & Plants / Conclusions
Ecology Vocabulary Exercise / Life Cycles / Bird Facts Table / Mammals Morphology compare
EcoCommunity Status in your state | Fields, Meadows and Fencerows eGame |
Citizen Scientist - Collect some data | Collecting data Activity doc. / pdf | Outside - In Showcase Project
Bats are our Buddies | Screech Owls Activity | Plan a School Habitat Garden Project | Bluebirds Project
Milkweeds & Monarch Butterfly Mania | Water and Watershed studies | Plants and People
Wildflowers info | Environmental Inquiry | Fields, Meadows & fencerows photos | Make an A to Z book
2000 Cynthia J. O'Hora This project may be freely use in a nonprofit setting.
Pennsylvania Science Anchors Science NetLinks Benchmark 5 - The Living Environment D. Interdependence of Life - " In all environments freshwater, marine, forest, desert, grassland, mountain, and others organisms with similar needs may compete with one another for resources, including food, space, water, air, and shelter. Two types of organisms may interact with one another in several ways: They may be in a producer/consumer, predator/prey, or parasite/host relationship." |
![]() Save a tree - use a Digital Answer format - Highlight the text of the title, directions and questions. Copy the text. Paste it in a word processing document. Save the document in your folder. Answer on the word processing document. Submit your assignment via an email attachment or class electronic dropbox.. Make Your Own Printed answer sheet.
Save a tree - use a Digital Answer format - Highlight the text of the title, directions and questions. Copy the text. Paste it in a word processing document. Save the document in your folder. Answer on the word processing document. Submit your assignment via an email attachment or class electronic dropbox.. Make Your Own Printed answer sheet.
The goal of this web project is to inform people through research and employing higher order thinking skills. This study unit encourages the use of free Internet information resources. Activities develop writing, information literacy, technology and mathematics skills. The resources posted here may be freely adapted or modified to meet each student's unique skills or interests.